Tigilanol tiglate (Stelfonta) is an injectable anti-cancer drug that is injected directly into eligible mast cell tumors and causes the destruction of tumor cells with great success.
Key Takeaways
- Tigilanol tiglate (Stelfonta) is a relatively new drug for mast cell tumors
- Tigilanol tiglate is directly injected into mast cell tumors in dogs.
- Your veterinarian will recommend the best treatment for mast cell tumors based on many factors, but Stelfonta may be a tool they recommend.
What Is Tigilanol Tiglate (Stelfonta)?
Tigilanol tiglate (brand name Stelfonta) is approved for use in dogs and is injected into mast cell tumors, disrupting cellular function and destroying tumor cells.1
Tigilanol tiglate is isolated from the seed of the Fontainea picrosperma tree.1 The drug disrupts normal cellular function, causing the cancer cells to die (oncolysis).1
Tigilanol tiglate is used in dogs to treat localized cutaneous (in the skin) mast cell tumors (MCTs) anywhere on the body and subcutaneous (below the skin) MCTs at or below the hock or elbow.1
Brand Names – Stelfonta
Stelfonta® is the brand name of tigilanol tiglate. It’s an injectable medication that is labeled exclusively for veterinary use. It is used exclusively for intertumoral (inside the tumor) injection for veterinary patients with localized mast cell tumors.1,2
How Tigilanol Tiglate in Dogs Works
Tigilanol tiglate, when injected into MCTs, causes rapid destruction of tumor cells through a process called hemorrhagic necrosis. This usually occurs in one to three days after injection.2
The death of the mast cells leads to the tumor dying and a wound developing as the tissue dies. This happens in the third to seven days post-injection.
The wound will heal through a process referred to as “second intention.”2,3
Second intention healing is when a wound is not closed, i.e. it remains open and heals more slowly.
Efforts to encourage healing and prevent infection may be necessary depending on the size of the wound and other factors.
Tigilanol tiglate has been found to create more minor wounds than surgical removal, even when the tumors are large.2
Post-treatment wound healing may take 4-6 weeks (about one and a half months).1
Common Uses of Tigilanol Tiglate in Dogs
Tigilanol tiglate has been found to be very effective in the resolution of local or single mast cell tumors.3
Tigilanol tiglate is used specifically for focal mast cell tumors (tumors that have not spread to other areas in the body) located within the skin anywhere on the body or beneath the skin at or below the elbow or the hock.1
Tigilanol Tiglate Results So Far
A 2019 study of 123 dogs with local mast cell tumors identified a 75% complete response rate after one treatment, and an 87-88% complete response rate with two treatments of tigilanol tiglate 84 days (about three months) post-treatment.3
Another recent study found of 64 dogs treated, 89% remained tumor-free at 12 months. The authors concluded that tigilanol tiglate provided a durable long-term response to local MCTs.4
The previously referenced studies found, in general, greater success with tigilanol tiglate therapy than with surgical removal.
When to Not Use Tigilanol Tiglate
Tigilanol tiglate is not used for all types of mast cell disease. Your veterinarian will be able to determine whether your dog’s tumor is a candidate.
If the MCT is ulcerated before injection, extreme caution should be used.1
As you’ll see below, some drugs must be used alongside tigilanol tiglate. However, unless prescribed by your veterinarian, the use of other antineoplastic agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, or immunosuppressants before or during therapy is not recommended.1
How Veterinarians Give Tigilanol Tiglate to Dogs
Tigilanol tiglate is administered by your veterinarian by injection directly into the tumor. Very specific placement of this medication within the tumor and appropriate dosing are imperative, so your veterinarian will carefully plan this process. Tigilanol tiglate is dosed based on the calculated volume of the tumor.1,2
A veterinarian performs the injection only at a veterinary facility.1 Typically, one injection is all that is necessary, but a second injection may be recommended based on your dog’s response.3
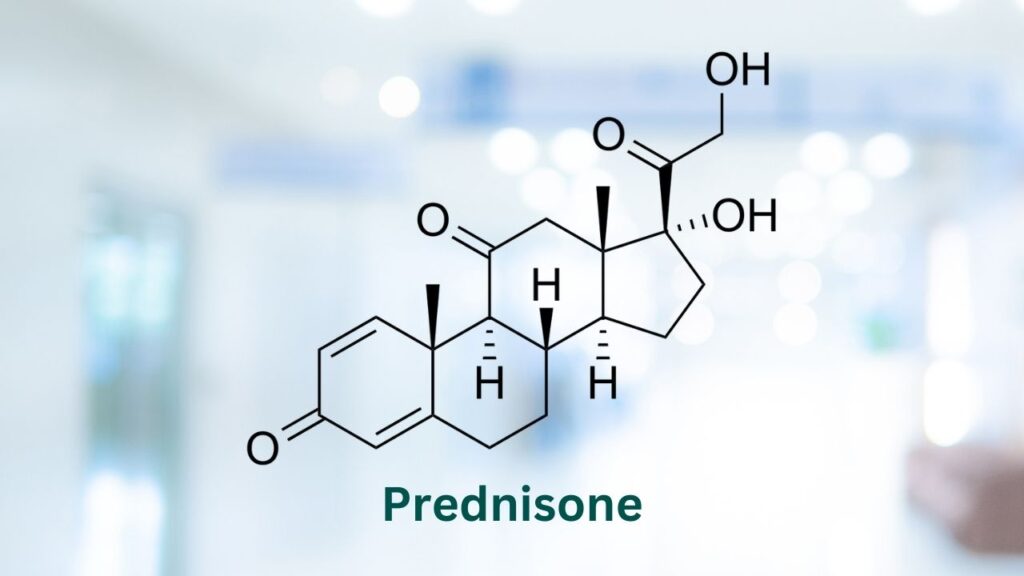
Tigilanol tiglate MUST be given with a steroid (such as prednisone or prednisolone), an antihistamine (such as diphenhydramine), and an antacid drug (such as famotidine).1
These medications help prevent severe, potentially life-threatening inflammatory responses that can be seen with mast cell destruction.
Please consult with your veterinarian regarding the dosing and timing of these medications before and during treatment.
What If I Miss a Dose?
Since the dosing schedule is usually one injection, possibly two, ‘missing a dose’ is typically not a problem.
Storage and Handling
A veterinarian must administer this drug at a veterinary facility. The proper handling of tigilanol tiglate will be the responsibility of your veterinarian and the veterinary facility.
Safety
Sedation may be necessary to allow safe administration.1
Avoid contact with your dog’s treatment site or any discharge from the site. Wash any soiled bedding separately and wear gloves when handling.1 Prevent other pets in the house from contact with the wound, wound discharge, or soiled bedding.1
Use of other antineoplastic agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, or immunosuppressants before or during therapy is not recommended unless recommended by your veterinarian as part of administering the injection.1
Tigilanol Tiglate Side Effects
Because of the tumor/cellular destruction within the tumor, the most common side effect of treatment is the development of a wound where the tumor was.3
Wounds were often found to be proportionate to the tumor size. Larger tumors made larger wounds, and smaller tumors made smaller wounds. Most wounds do not require bandaging or aggressive treatments.3
Post-injection pain, swelling, inflammation, and tissue loss are common. Additionally, lameness associated with the affected limb and gastrointestinal upset may occur.1,3 Secondary infections are uncommon, but possible.3
Your veterinarian will be sure to instruct you on how to care for the wound.
Topics
Did You Find This Helpful? Share It with Your Pack!
Use the buttons to share what you learned on social media, download a PDF, print this out, or email it to your veterinarian.